Understanding the Indian Railways’ Digital Business Development Platform
Posted: 23 May 2022 | Raman Arora | No comments yet
Raman Arora, Principal Project Engineer in the Centre for Railway Information Systems (CRIS) – an IT arm of India’s Ministry of Railways, offers an overview of the Indian Railways’ Digital Business Development Platform and what benefits it can offer its users.


Being an integral part of India’s logistics ecosystem, railway transportation plays a vital role in facilitating trade and business in the country. An efficient railway system lowers the cost of transportation, integrates people and markets across the country, links backward regions with the mainstream economy (by opening them up to trade and investment), and thereby increases the overall productivity and global competitiveness of the economy.
Railway transportation is also an essential component of intermodal supply chains. Indian Railways is considered the backbone of the country’s logistics sector. Indian Railways’ freight network comprises the effective management of rolling stock including 3,30,000 wagons, with over 12,000 locomotives including more than 5,000 freight trains which operate on a daily basis.
The market share of Indian Railways’ freight transportation is approximately 30 per cent. The competitive logistics sector and rapid industrialisation leading to rising demands is challenging Indian Railways to continuously deliver innovation and to gain the maximum market share in freight transportation in India.
Indian Railways have a three-tier structure to manage its mammoth operations. The Railway Board is at the apex level. There are 17 zones which are further subdivided into 69 divisions at the field level. In order to leap forward in its endeavours, national Business Development Units (BDUs) have been established by Indian Railways at divisional, zonal and railway board levels. Multi-disciplinary teams from BDUs are reaching out to customers to attract new business, by providing appealing value-for-money logistics solutions. The BDUs have started showing signs of successes in their efforts towards this common objective. Indian Railways has recorded its highest ever loading of 1.418 billion tonnes in the year 2021-2022, with a new target of 1.7 billion tonnes for the year 2022-2023.
In order to gain momentum and to analyse, monitor and expedite the proceedings of BDUs, Indian Railways has embraced technology as a cardinal tool. The Centre for Railway Information Systems (CRIS), the IT arm of Indian Railways, has developed an online BDU Portal where railway field users can report, connect, share and propose various ideas/proposals, action plans and innovations for business development. The design philosophy behind the portal is that divisional (field) users possess the maximum information about business opportunities in their local area. This information needs to be aggregated at zonal and railway board levels so that a holistic marketing strategy can be developed to capture more business. The portal connects divisional BDUs to their zonal counterparts and to the railway board. Data reported by BDUs play a vital role in identifying the gaps and also help fuel the process of formulating effective strategies for the future.
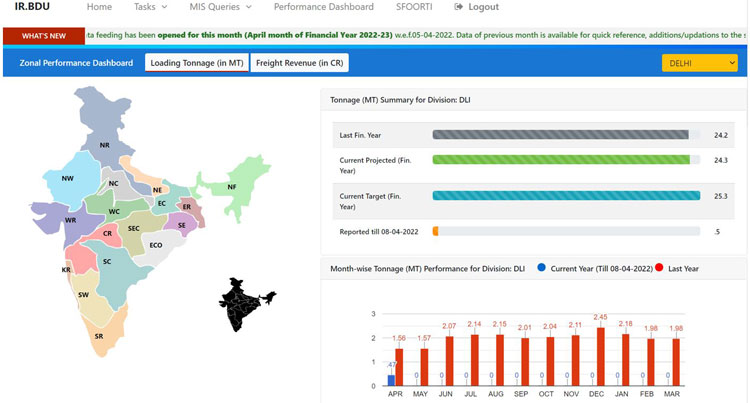

Figure 1: Screenshot of the IRBDU Dashboard
Distinguishing features of Indian Railways’ IRBDU Portal
The portal is available to three sets of users: Divisional BDUs, Zonal BDUs and the Railway Board. With their designated credentials, they may login to it and report/access the information available through various sources. The distinguishing features of the portal are as follows:
IRBDU Dashboard
The dashboard is the opening page of the portal, immediately after successful login. The dashboard presents a comprehensive view of zonal as well as divisional performance in terms of loading (in tonnage) and revenue (in rupee crores), targets set for the year, projections, progress so far and the last year analysis, commodity wise, month-wise performance and Rail Coefficients (percentage share of railways w.r.t. total freight generation) of various commodities in respective regions. Information can be viewed at Indian Railways level and can also be drilled down to divisional levels.
Tasks
The ‘task’ function of the portal gives field users the ability to feed specified data in the form of business development plan, business proposals, resource centre and rail coefficient as follows:
Business development and acquisition plan
Data is captured from field level BDUs on multiple aspects, such as loading/freight projections for the current financial year, comparison of cost of transporting commodities by rail and road (per tonne km basis), industry clusters in that regions with rail coefficients of commodities being carried, action plans and BDU initiatives in order to increase loadings, currently associated and proposed logistics partners, SWOT analysis for that region, level of industry outreach and quantum of traffic expected. The task also captures data on target areas for business development.
Business proposals
Under this task, field users can submit business proposals and initiatives which need the approval of zonal railways or the railway board. The proposals can be examined, and decisions can be shared digitally on the portal where all the field users can view the decisions on business development proposals and can take action for business development in their own area.
Resource Centre
The field users are supposed to feed information about customers, freight aggregators, and industry representatives available in their area. The Resource Centre holds a directory of such industry resources, which can be accessed by all the user for further marketing purposes.
Rail coefficients
The IRBDU portal is being actively used as a digital platform to report business development opportunities, monitor their progress and to fuel the multifaceted approaches of BDUs.
The share of railways in the transportation of a commodity is measured in terms of rail coefficient which is the ratio of loading by railways to total despatch of a commodity in a given region like division, zone over a period of time. Field level BDUs report the change in Rail Coefficient for the set of commodities being carried in that region, on a year-on-year basis. The data helps in monitoring the effectiveness of initiatives being taken towards business enhancements in that region.
The data in the system is fed/updated on a monthly basis to assess the efficacy of the ongoing improvements and to monitor the current status of various initiatives and action plans. For the convenience of users, every task in the system holds an elaborate explanation on how to feed the data for that screen. A detailed user manual is also available in the system to provide the know-how, citing the purpose of each task and MIS report of the portal.
Management Information System (MIS) Reports
The portal also provides an extensive set of MIS reports to analyse and monitor the growth of freight business across Indian Railways. The platform facilitates identifying the gaps and the necessary actions to take to bridge them.
Business proposals
The MIS provides a summary of all the business proposals submitted by field users and action taken on them. In order to expedite the progress, higher authorities could sanction/take necessary actions towards the received proposals and communicate the decisions through this portal itself.
Rail/Road comparison
This MIS offers a comparative analysis of the cost of transportation by rail and road (including the first-mile last-mile cost and other handling costs) for carrying different commodities. Information available through this report may help railway users to rationalise freight charges and to formulate a marketing strategy to shift cargo from road to rail.
Measures of progress
This MIS presents a snapshot of the expected increase in traffic through BDUs action plans, initiatives, and industry outreach. The effectiveness of BDU initiatives can also be assessed through this MIS.
Traffic plans
This MIS provides an overview of important ongoing works for business development, their benefits, associated costs, length and targets for completion targets. The railway board and zonal railways can monitor the progress of these works and can also analyse impact of these works on business development.
Customer proposals
The freight customers can also submit proposals to offer new traffic on the Indian Railways website. These business proposals can be viewed by all the railway users. The customer can directly reach BDUs through this option. The BDUs can take appropriate action on these business proposals to attract more traffic.
Divisional statistics
This view presents the freight loading and earning progress of Indian Railways’ divisions over a month-on-month basis. The information available helps to ascertain the alignment of divisions with their assigned yearly loading targets.
Business development analysis
This MIS facilitates monitoring of business growth for a selected commodity over a zone or over the entire Indian Railways network.
All the MIS reports provide month-on-month progress analysis, as reported by divisional BDUs. In order to facilitate deeper analysis of various aspects, number of filters are available for customised access.
The IRBDU portal is being actively used as a digital platform to report business development opportunities, monitor their progress and to fuel the multifaceted approaches of BDUs. Many of the processes which hitherto required submission/forwarding of physical documents have moved to digital means. Thus, the portal is emerging as a game changer to facilitate BDUs, moving swiftly towards the fulfilment of Indian Railways’ freight business objectives.


Raman Arora has approximately 17 years of experience in the field of ICT applications and e-Governance solutions. He has played a key role in digital transformation of various aspects of Indian Railways Freight Business operations along with a number of G2B, G2C and G2G data integrations. He has developed several dashboards, decision support systems, GIS, web, and mobile applications. He is MBA in Technology Management (IIT Delhi) and B.Tech. in Computer Science and Engineering. Views presented in this article are personal.
Related topics
Cargo, Freight & Heavy-Haul, Digitalisation, Technology & Software, The Supply Chain, The Workforce