HS2 reveals carbon saving modular design for Thame Valley Viaduct
Posted: 6 April 2022 | Elliot Robinson (Editorial Assistant - Global Railway Review) | No comments yet
HS2 have revealed the new modular design of the Thame Valley Viaduct which will cut the construction carbon footprint by two-thirds.
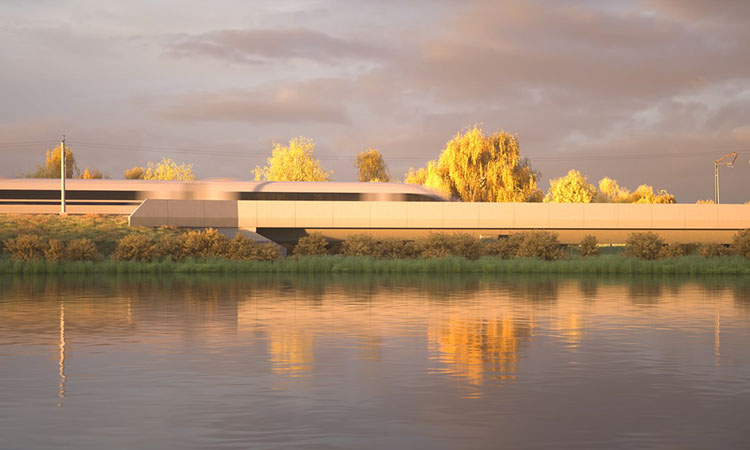


Credit: HS2 - Artist's impression of the Thame Valley Viaduct in ten years time
HS2 has revealed the final designs for the Thame Valley Viaduct and the pioneering prefabricated construction methods that will see the 880m long structure slotted together like a giant Lego set, cutting its carbon footprint by an estimated 66 per cent. Crossing the flood plain of the River Thame, just outside Aylesbury, the viaduct will carry HS2 trains at speeds of up to 360km/h between London, Birmingham and the North.
The underside of the viaduct will be just 3m above the ground, with thirty-six 25m long neat and even spans crossing the river and surrounding wetlands. The piers will be extended to almost connect with the parapet edge, helping to enhance the appearance of a light and narrow structure. Thame Valley is one of 15 viaducts designed by HS2 Ltd’s main works contractor, EKFB (a team made up of Eiffage, Kier, Ferrovial Construction and BAM Nuttall), working with their design partner, ASC (a joint venture between Arcadis Setec and COWI) and specialist architects Moxon.
“HS2 trains and stations will be zero carbon from day one, providing a cleaner, greener way to travel and helping the fight against climate change,” Tomas Garcia, Head of Civil Structures for HS2, said. “We are also serious about reducing the amount of carbon we use during construction, and Thame Valley is a great example of how our contractors are using the latest engineering techniques to do just that. Prefabrication and off-site manufacturing offer huge benefits in terms of efficiency and this design will help us deliver a more efficient, durable and elegant structure with less concrete and steel.”
In a major step forward for viaduct design in the UK, the team opted for two wide box girder beams per span instead of eight smaller beams, to simplify and speed up assembly. The production of steel and concrete is a major contributor to carbon emissions, with the new lighter-weight structure expected to save 19,000 tonnes of embedded carbon in comparison to the previous design. As well as cutting embedded carbon in terms of materials, this approach requires less lorries to deliver material to site, cuts waste and will reduce disruption for the community during construction.
In an unusual move, the 35 concrete piers that support the viaduct will also be entirely made off site before being placed on their foundations, meaning that every major element of the structure will be prefabricated. Traditionally, viaduct beams are secured together above each of the piers with a concrete diaphragm which is cast in situ. The larger pre-cast beams that will be used at Thame Valley can secured directly to one another, removing the need for the diaphragm, improving durability and reliability, saving time, cutting cost, and improving safety by reducing the need for people to work at height.
“The Thame Valley Viaduct has been conceived as a minimalist elevated causeway passing low over the flood plain of the River Thame,” Ben Addy, Managing Director of Moxon, said. “This approach relies upon refinement of detail and has been enabled by the advanced engineering and construction techniques developed by the team. The result is a low key and elegant sequence of spans punctuated by thirty-four pairs of piers cradling the deck.”
Around the viaduct, the river floodplain will be enhanced to boost biodiversity and help better manage flood water. This will include replacing existing arable land with new wildlife-rich areas of woodland and wetland.
Related topics
High Speed Two (HS2), Infrastructure Developments, Sustainability/Decarbonisation, Track/Infrastructure Maintenance & Engineering